在 Spring Boot 中做权限管理,一般来说,主流的方案是 Spring Security ,但是,仅仅从技术角度来说,也可以使用 Shiro。
今天松哥就来和大家聊聊 Spring Boot 整合 Shiro 的话题!
一般来说,Spring Security 和 Shiro 的比较如下:
Spring Security 是一个重量级的安全管理框架;Shiro 则是一个轻量级的安全管理框架
Spring Security 概念复杂,配置繁琐;Shiro 概念简单、配置简单
Spring Security 功能强大;Shiro 功能简单
…
虽然 Shiro 功能简单,但是也能满足大部分的业务场景。所以在传统的 SSM 项目中,一般来说,可以整合 Shiro。
在 Spring Boot 中,由于 Spring Boot 官方提供了大量的非常方便的开箱即用的 Starter ,当然也提供了 Spring Security 的 Starter ,使得在 Spring Boot 中使用 Spring Security 变得更加容易,甚至只需要添加一个依赖就可以保护所有的接口,所以,如果是 Spring Boot 项目,一般选择 Spring Security 。
这只是一个建议的组合,单纯从技术上来说,无论怎么组合,都是没有问题的。
在 Spring Boot 中整合 Shiro ,有两种不同的方案:
第一种就是原封不动的,将 SSM 整合 Shiro 的配置用 Java 重写一遍。
第二种就是使用 Shiro 官方提供的一个 Starter 来配置,但是,这个 Starter 并没有简化多少配置。
原生的整合
创建一个 Spring Boot 项目,只需要添加 Web 依赖即可:
项目创建成功后,加入 Shiro 相关的依赖,完整的 pom.xml 文件中的依赖如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.shiro</groupId > <artifactId > shiro-web</artifactId > <version > 1.4.0</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.shiro</groupId > <artifactId > shiro-spring</artifactId > <version > 1.4.0</version > </dependency > </dependencies >
接下来我们来自定义核心组件 Realm:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public class MyRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo (PrincipalCollection principals) { return null ; } @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo (AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { String username = (String) token.getPrincipal(); if (!"javaboy" .equals(username)) { throw new UnknownAccountException ("账户不存在!" ); } return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo (username, "123" , getName()); } }
在 Realm 中实现简单的认证操作即可,不做授权,授权的具体写法和 SSM 中的 Shiro 一样,不赘述。这里的认证表示用户名必须是 javaboy ,用户密码必须是 123 ,满足这样的条件,就能登录成功!
接下来进行 Shiro 的配置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 @Configuration public class ShiroConfig { @Bean MyRealm myRealm () { return new MyRealm (); } @Bean SecurityManager securityManager () { DefaultWebSecurityManager manager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager (); manager.setRealm(myRealm()); return manager; } @Bean ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean () { ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean (); bean.setSecurityManager(securityManager()); bean.setLoginUrl("/login" ); bean.setSuccessUrl("/index" ); bean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/unauthorizedurl" ); Map<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap <>(); map.put("/doLogin" , "anon" ); map.put("/**" , "authc" ); bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map); return bean; } }
在这里进行 Shiro 的配置主要配置 3 个 Bean :
首先需要提供一个 Realm 的实例。
需要配置一个 SecurityManager,在 SecurityManager 中配置 Realm。
配置一个 ShiroFilterFactoryBean ,在 ShiroFilterFactoryBean 中指定路径拦截规则等。
配置登录和测试接口。
其中,ShiroFilterFactoryBean 的配置稍微多一些,配置含义如下:
setSecurityManager 表示指定 SecurityManager。
setLoginUrl 表示指定登录页面。
setSuccessUrl 表示指定登录成功页面。
接下来的 Map 中配置了路径拦截规则,注意,要有序。
这些东西都配置完成后,接下来配置登录 Controller:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 @RestController public class LoginController { @PostMapping("/doLogin") public void doLogin (String username, String password) { Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); try { subject.login(new UsernamePasswordToken (username, password)); System.out.println("登录成功!" ); } catch (AuthenticationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("登录失败!" ); } } @GetMapping("/hello") public String hello () { return "hello" ; } @GetMapping("/login") public String login () { return "please login!" ; } }
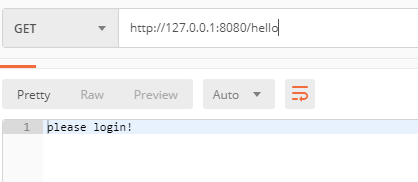
测试时,首先访问 /hello 接口,由于未登录,所以会自动跳转到 /login 接口:
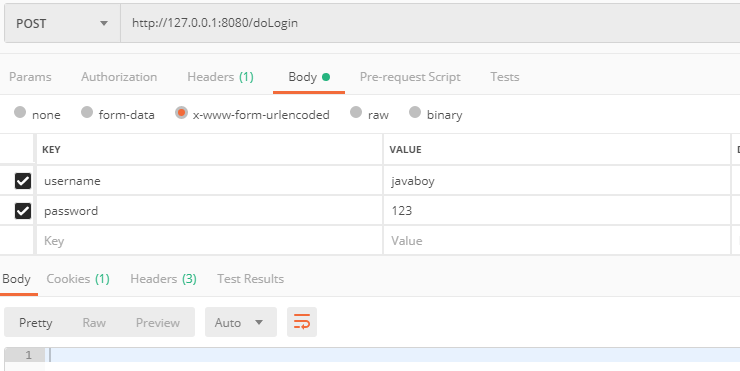
然后调用 /doLogin 接口完成登录:
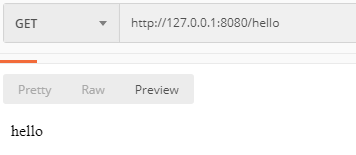
再次访问 /hello 接口,就可以成功访问了:
使用 Shiro Starter 上面这种配置方式实际上相当于把 SSM 中的 XML 配置拿到 Spring Boot 中用 Java 代码重新写了一遍,除了这种方式之外,我们也可以直接使用 Shiro 官方提供的 Starter 。
创建成功后,添加 shiro-spring-boot-web-starter ,这个依赖可以代替之前的 shiro-web 和 shiro-spring 两个依赖,pom.xml 文件如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.shiro</groupId > <artifactId > shiro-spring-boot-web-starter</artifactId > <version > 1.4.0</version > </dependency > </dependencies >
这里的 Realm 和前面的一样,我就不再赘述。
接下来在 application.properties 中配置 Shiro 的基本信息:
1 2 3 4 5 6 shiro.sessionManager.sessionIdCookieEnabled =true shiro.sessionManager.sessionIdUrlRewritingEnabled =true shiro.unauthorizedUrl =/unauthorizedurl shiro.web.enabled =true shiro.successUrl =/index shiro.loginUrl =/login
配置解释:
第一行表示是否允许将sessionId 放到 cookie 中
第二行表示是否允许将 sessionId 放到 Url 地址拦中
第三行表示访问未获授权的页面时,默认的跳转路径
第四行表示开启 shiro
第五行表示登录成功的跳转页面
第六行表示登录页面
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 @Configuration public class ShiroConfig { @Bean MyRealm myRealm () { return new MyRealm (); } @Bean DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager () { DefaultWebSecurityManager manager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager (); manager.setRealm(myRealm()); return manager; } @Bean ShiroFilterChainDefinition shiroFilterChainDefinition () { DefaultShiroFilterChainDefinition definition = new DefaultShiroFilterChainDefinition (); definition.addPathDefinition("/doLogin" , "anon" ); definition.addPathDefinition("/**" , "authc" ); return definition; } }
这里的配置和前面的比较像,但是不再需要 ShiroFilterFactoryBean 实例了,替代它的是 ShiroFilterChainDefinition ,在这里定义 Shiro 的路径匹配规则即可。
这里定义完之后,接下来的登录接口定义以及测试方法都和前面的一致,我就不再赘述了。大家可以参考上文。
总结 本文主要向大家介绍了 Spring Boot 整合 Shiro 的两种方式,一种是传统方式的 Java 版,另一种则是使用 Shiro 官方提供的 Starter,两种方式,不知道大家有没有学会呢?
本文案例,我已经上传到 GitHub ,欢迎大家 star:https://github.com/lenve/javaboy-code-samples
关于本文,有问题欢迎留言讨论。