Spring Boot2 系列教程(一)纯 Java 搭建 SSM 项目
在 Spring Boot 项目中,正常来说是不存在 XML 配置,这是因为 Spring Boot 不推荐使用 XML ,注意,并非不支持,Spring Boot 推荐开发者使用 Java 配置来搭建框架,Spring Boot 中,大量的自动化配置都是通过 Java 配置来实现的,这一套实现方案,我们也可以自己做,即自己也可以使用纯 Java 来搭建一个 SSM 环境,即在项目中,不存在任何 XML 配置,包括 web.xml 。
环境要求:
- 使用纯 Java 来搭建 SSM 环境,要求 Tomcat 的版本必须在 7 以上。
快速体验
1 创建工程
创建一个普通的 Maven 工程(注意,这里可以不必创建 Web 工程),并添加 SpringMVC 的依赖,同时,这里环境的搭建需要用到 Servlet ,所以我们还需要引入 Servlet 的依赖(一定不能使用低版本的 Servlet),最终的 pom.xml 文件如下:
1 | <dependency> |
2 添加 Spring 配置
工程创建成功之后,首先添加 Spring 的配置文件,如下:
1 |
|
关于这个配置,我说如下几点:
- @Configuration 注解表示这是一个配置类,在我们这里,这个配置的作用类似于 applicationContext.xml
- @ComponentScan 注解表示配置包扫描,里边的属性和 xml 配置中的属性都是一一对应的,useDefaultFilters 表示使用默认的过滤器,然后又除去 Controller 注解,即在 Spring 容器中扫描除了 Controller 之外的其他所有 Bean 。
3 添加 SpringMVC 配置
接下来再来创建 springmvc 的配置文件:
1 |
|
注意,如果不需要在 SpringMVC 中添加其他的额外配置,这样就可以了。即 视图解析器、JSON 解析、文件上传……等等,如果都不需要配置的话,这样就可以了。
4 配置 web.xml
此时,我们并没有 web.xml 文件,这时,我们可以使用 Java 代码去代替 web.xml 文件,这里会用到 WebApplicationInitializer ,具体定义如下:
1 | public class WebInit implements WebApplicationInitializer { |
WebInit 的作用类似于 web.xml,这个类需要实现 WebApplicationInitializer 接口,并实现接口中的方法,当项目启动时,onStartup 方法会被自动执行,我们可以在这个方法中做一些项目初始化操作,例如加载 SpringMVC 容器,添加过滤器,添加 Listener、添加 Servlet 等。
注意:
由于我们在 WebInit 中只是添加了 SpringMVC 的配置,这样项目在启动时只会去加载 SpringMVC 容器,而不会去加载 Spring 容器,如果一定要加载 Spring 容器,需要我们修改 SpringMVC 的配置,在 SpringMVC 配置的包扫描中也去扫描 @Configuration 注解,进而加载 Spring 容器,还有一种方案可以解决这个问题,就是直接在项目中舍弃 Spring 配置,直接将所有配置放到 SpringMVC 的配置中来完成,这个在 SSM 整合时是没有问题的,在实际开发中,较多采用第二种方案,第二种方案,SpringMVC 的配置如下:
1 |
|
这种方案中,所有的注解都在 SpringMVC 中扫描,采用这种方案的话,则 Spring 的配置文件就可以删除了。
5 测试
最后,添加一个 HelloController ,然后启动项目进行测试:
1 |
|
启动项目,访问接口,结果如下:
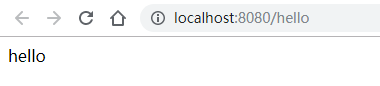
6 其他配置
6.1 静态资源过滤
静态资源过滤在 SpringMVC 的 XML 中的配置如下:
1 | <mvc:resources mapping="/**" location="/"/> |
在 Java 配置的 SSM 环境中,如果要配置静态资源过滤,需要让 SpringMVC 的配置继承 WebMvcConfigurationSupport ,进而重写 WebMvcConfigurationSupport 中的方法,如下:
1 |
|
重写 addResourceHandlers 方法,在这个方法中配置静态资源过滤,这里我将静态资源放在 resources 目录下,所以资源位置是 classpath:/ ,当然,资源也可以放在 webapp 目录下,此时只需要修改配置中的资源位置即可。如果采用 Java 来配置 SSM 环境,一般来说,可以不必使用 webapp 目录,除非要使用 JSP 做页面模板,否则可以忽略 webapp 目录。
6.2 视图解析器
在 XML 文件中,通过如下方式配置视图解析器:
1 | <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> |
如果通过 Java 类,一样也可以实现类似功能。
首先为我们的项目添加 webapp 目录,webapp 目录中添加一个 jsp 目录,jsp 目录中添加 jsp 文件:
然后引入 JSP 的依赖:
1 | <dependency> |
然后,在配置类中,继续重写方法:
1 |
|
接下来,在 Controller 中添加控制器即可访问 JSP 页面:
1 |
|
6.3 路径映射
有的时候,我们的控制器的作用仅仅只是一个跳转,就像上面小节中的控制器,里边没有任何业务逻辑,像这种情况,可以不用定义方法,可以直接通过路径映射来实现页面访问。如果在 XML 中配置路径映射,如下:
1 | <mvc:view-controller path="/hello" view-name="hello" status-code="200"/> |
这行配置,表示如果用户访问 /hello 这个路径,则直接将名为 hello 的视图返回给用户,并且响应码为 200,这个配置就可以替代 Controller 中的方法。
相同的需求,如果在 Java 代码中,写法如下:
1 |
|
此时,用户访问 /hello3 接口,就能看到名为 hello 的视图文件。
6.4 JSON 配置
SpringMVC 可以接收JSON 参数,也可以返回 JSON 参数,这一切依赖于 HttpMessageConverter。
HttpMessageConverter 可以将一个 JSON 字符串转为 对象,也可以将一个对象转为 JSON 字符串,实际上它的底层还是依赖于具体的 JSON 库。
所有的 JSON 库要在 SpringMVC 中自动返回或者接收 JSON,都必须提供和自己相关的 HttpMessageConverter 。
SpringMVC 中,默认提供了 Jackson 和 gson 的 HttpMessageConverter ,分别是:MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter 和 GsonHttpMessageConverter 。
正因为如此,我们在 SpringMVC 中,如果要使用 JSON ,对于 jackson 和 gson 我们只需要添加依赖,加完依赖就可以直接使用了。具体的配置是在 AllEncompassingFormHttpMessageConverter 类中完成的。
如果开发者使用了 fastjson,那么默认情况下,SpringMVC 并没有提供 fastjson 的 HttpMessageConverter ,这个需要我们自己提供,如果是在 XML 配置中,fastjson 除了加依赖,还要显式配置 HttpMessageConverter,如下:
1 | <mvc:annotation-driven> |
在 Java 配置的 SSM 中,我们一样也可以添加这样的配置:
1 |
|
然后,就可以在接口中直接返回 JSON 了,此时的 JSON 数据将通过 fastjson 生成。
总结
好了,本文通过一个简单的例子向读者展示了使用 Java 来配置 Spring+SpringMVC 环境,事实上,只要这两个配置 OK ,再加入 MyBatis 就是非常容易的事了,本文相关的案例松哥已经上传到 GitHub 上了:https://github.com/lenve/javaboy-code-samples。
关于本文,有问题欢迎留言讨论。
