Spring Boot2 系列教程(十三)Spring Boot 中的全局异常处理
在 Spring Boot 项目中 ,异常统一处理,可以使用 Spring 中 @ControllerAdvice 来统一处理,也可以自己来定义异常处理方案。Spring Boot 中,对异常的处理有一些默认的策略,我们分别来看。
默认情况下,Spring Boot 中的异常页面 是这样的:
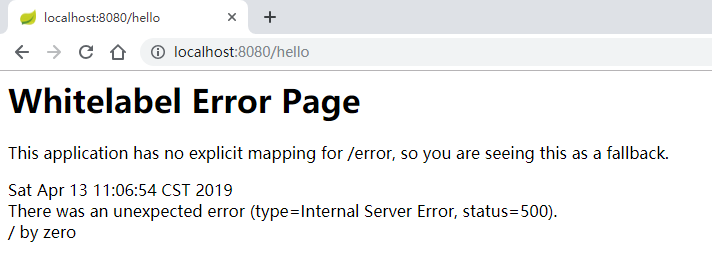
我们从这个异常提示中,也能看出来,之所以用户看到这个页面,是因为开发者没有明确提供一个 /error 路径,如果开发者提供了 /error 路径 ,这个页面就不会展示出来,不过在 Spring Boot 中,提供 /error 路径实际上是下下策,Spring Boot 本身在处理异常时,也是当所有条件都不满足时,才会去找 /error 路径。那么我们就先来看看,在 Spring Boot 中,如何自定义 error 页面,整体上来说,可以分为两种,一种是静态页面,另一种是动态页面。
静态异常页面
自定义静态异常页面,又分为两种,第一种 是使用 HTTP 响应码来命名页面,例如 404.html、405.html、500.html ….,另一种就是直接定义一个 4xx.html,表示400-499 的状态都显示这个异常页面,5xx.html 表示 500-599 的状态显示这个异常页面。
默认是在 classpath:/static/error/ 路径下定义相关页面:
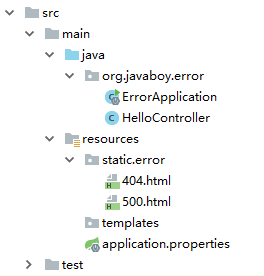
此时,启动项目,如果项目抛出 500 请求错误,就会自动展示 500.html 这个页面,发生 404 就会展示 404.html 页面。如果异常展示页面既存在 5xx.html,也存在 500.html ,此时,发生500异常时,优先展示 500.html 页面。
动态异常页面
动态的异常页面定义方式和静态的基本 一致,可以采用的页面模板有 jsp、freemarker、thymeleaf。动态异常页面,也支持 404.html 或者 4xx.html ,但是一般来说,由于动态异常页面可以直接展示异常详细信息,所以就没有必要挨个枚举错误了 ,直接定义 4xx.html(这里使用thymeleaf模板)或者 5xx.html 即可。
注意,动态页面模板,不需要开发者自己去定义控制器,直接定义异常页面即可 ,Spring Boot 中自带的异常处理器会自动查找到异常页面。
页面定义如下:
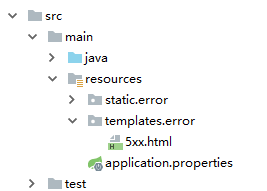
页面内容如下:
1 |
|
默认情况下,完整的异常信息就是这5条,展示 效果如下 :
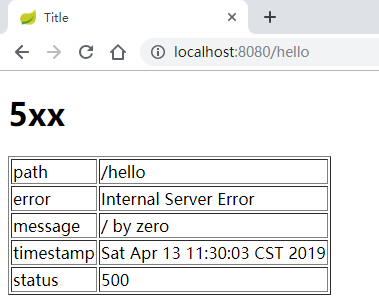
如果动态页面和静态页面同时定义了异常处理页面,例如 classpath:/static/error/404.html 和 classpath:/templates/error/404.html 同时存在时,默认使用动态页面。即完整的错误页面查找方式应该是这样:
发生了 500 错误–>查找动态 500.html 页面–>查找静态 500.html –> 查找动态 5xx.html–>查找静态 5xx.html。
自定义异常数据
默认情况下,在 Spring Boot 中,所有的异常数据其实就是上文所展示出来的 5 条数据,这 5 条数据定义在 org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.error.DefaultErrorAttributes 类中,具体定义在 getErrorAttributes 方法中 :
1 |
|
DefaultErrorAttributes 类本身则是在 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration 异常自动配置类中定义的,如果开发者没有自己提供一个 ErrorAttributes 的实例的话,那么 Spring Boot 将自动提供一个 ErrorAttributes 的实例,也就是 DefaultErrorAttributes 。
基于此 ,开发者自定义 ErrorAttributes 有两种方式 :
- 直接实现 ErrorAttributes 接口
- 继承 DefaultErrorAttributes(推荐),因为 DefaultErrorAttributes 中对异常数据的处理已经完成,开发者可以直接使用。
具体定义如下:
1 |
|
定义好的 ErrorAttributes 一定要注册成一个 Bean ,这样,Spring Boot 就不会使用默认的 DefaultErrorAttributes 了,运行效果如下图:
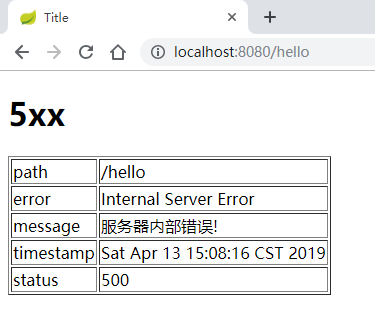
自定义异常视图
异常视图默认就是前面所说的静态或者动态页面,这个也是可以自定义的,首先 ,默认的异常视图加载逻辑在 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.BasicErrorController 类的 errorHtml 方法中,这个方法用来返回异常页面+数据,还有另外一个 error 方法,这个方法用来返回异常数据(如果是 ajax 请求,则该方法会被触发)。
1 |
|
在该方法中 ,首先会通过 getErrorAttributes 方法去获取异常数据(实际上会调用到 ErrorAttributes 的实例 的 getErrorAttributes 方法),然后调用 resolveErrorView 去创建一个 ModelAndView ,如果这里创建失败,那么用户将会看到默认的错误提示页面。
正常情况下, resolveErrorView 方法会来到 DefaultErrorViewResolver 类的 resolveErrorView 方法中:
1 |
|
在这里,首先以异常响应码作为视图名分别去查找动态页面和静态页面,如果没有查找到,则再以 4xx 或者 5xx 作为视图名再去分别查找动态或者静态页面。
要自定义异常视图解析,也很容易 ,由于 DefaultErrorViewResolver 是在 ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration 类中提供的实例,即开发者没有提供相关实例时,会使用默认的 DefaultErrorViewResolver ,开发者提供了自己的 ErrorViewResolver 实例后,默认的配置就会失效,因此,自定义异常视图,只需要提供 一个 ErrorViewResolver 的实例即可:
1 |
|
实际上,开发者也可以在这里定义异常数据(直接在 resolveErrorView 方法重新定义一个 model ,将参数中的model 数据拷贝过去并修改,注意参数中的 model 类型为 UnmodifiableMap,即不可以直接修改),而不需要自定义 MyErrorAttributes。定义完成后,提供一个名为 123 的视图,如下图:
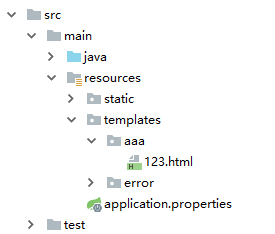
如此之后,错误试图就算定义成功了。
总结
实际上也可以自定义异常控制器 BasicErrorController ,不过松哥觉得这样太大动干戈了,没必要,前面几种方式已经可以满足我们的大部分开发需求了。如果是前后端分离架构,异常处理还有其他一些处理方案,这个松哥以后和大家聊。
