在 Spring Security 中,我就想从子线程获取用户登录信息,怎么办?
大家知道在 Spring Security 中想要获取登录用户信息,不能在子线程中获取,只能在当前线程中获取,其中一个重要的原因就是 SecurityContextHolder 默认将用户信息保存在 ThreadLocal 中。
但是实际上 SecurityContextHolder 一共定义了三种存储策略:
1 | public class SecurityContextHolder { |
第二种存储策略 MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL 就支持在子线程中获取当前登录用户信息,而 MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL 的底层使用的就是 InheritableThreadLocal,那么 InheritableThreadLocal 和 ThreadLocal 有什么区别呢?为什么它就可以支持从子线程中获取数据呢?今天松哥就来和大家聊一聊这个话题。这个问题搞懂了,就理解了为什么在 Spring Security 中,只要我们稍加配置,就可以在子线程中获取到当前登录用户信息。
1.抛出问题
先来看一个大家可能都见过的例子:
1 |
|
这段代码的打印结果,相信大家都很清楚:
1 | threadLocal.get() = javaboy |
数据在哪个线程存储,就要从哪个线程读取,子线程是读取不到的。如果我们把上面案例中的 ThreadLocal 修改为 InheritableThreadLocal,如下:
1 |
|
此时的运行结果就会发生变化,如下:
1 | threadLocal.get() = javaboy |
可以看到,如果使用了 InheritableThreadLocal,即使在子线程中也能获取到父线程 ThreadLocal 中的数据。
那么这是怎么回事呢?我们一起来分析一下。
2.ThreadLocal
我们先来分析一下 ThreadLocal。
不看源码,仅从使用的角度来分析 ThreadLocal,大家会发现一个 ThreadLocal 只能存储一个对象,如果你需要存储多个对象,就需要多个 ThreadLocal 。
我们通过 ThreadLocal 源码来分析下。
当我们想要去调用 set 方法存储一个对象时,如下:
1 | public void set(T value) { |
大家可以看到,存储的时候会首先获取到一个 ThreadLocalMap 对象,获取的时候需要传入当前线程,看到这里大家可能就猜出来几分了,数据存储在一个类似于 Map 的 ThreadLocalMap 中,ThreadLocalMap 又和线程关联起来,怪不得每个线程只能获取到自己的数据。接下来我们来验证一下,继续看 getMap 方法:
1 | ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) { |
getMap 方法返回的是一个 threadLocals 变量,也就是说,数据是存在 threadLocals 中的。threadLocals 则就是一个 ThreadLocalMap。数据存入 ThreadLocalMap 实际上是保存在一个 Entry 数组中。在同一个线程中,一个 ThreadLocal 只能保存一个对象,如果需要保存多个对象,就需要多个 ThreadLocal,同一个线程中的多个 ThreadLocal 最终所保存的变量实际上在同一个 ThreadLocalMap 即同一个 Entry 数组之中。不同线程的 ThreadLocal 所保存的变量在不同的 Entry 数组中。Entry 数组中的 key 实际上就是 ThreadLocal 对象,value 则是 set 进来的数据。
我们再来看下数据读取:
1 | public T get() { |
首先根据当前线程获取到对应的 ThreadLocalMap,再传入当前对象获取到 Entry,然后将 Entry 对象中的 value 返回即可。有人可能会问,Entry 不是一个数组吗?为什么不传入一个数组下标去获取 Entry ,而是通过当前 ThreadLocal 对象去获取 Entry 呢?其实在 getEntry 方法中,就是根据当前对象计算出数组下标,然后将获取到的 Entry 返回。
3.InheritableThreadLocal
InheritableThreadLocal 实际上是 ThreadLocal 的子类,我们来看下 InheritableThreadLocal 的定义:
1 | public class InheritableThreadLocal<T> extends ThreadLocal<T> { |
可以看到,主要就是重写了三个方法。getMap 方法的返回值变成了 inheritableThreadLocals 对象,createMap 方法中,构建出来的 inheritableThreadLocals 还依然是 ThreadLocalMap 的对象。和 ThreadLocal 相比,主要是保存数据的对象从 threadLocals 变为 inheritableThreadLocals。
这样的变化,对于前面的我们所说的 ThreadLocal 中的 get/set 并不影响,也就是 ThreadLocal 的特性依然不变。
变化发生在线程的初始化方法里,我们来看一下 Thread#init 方法:
1 | private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, |
可以看到,在创建子线程的时候,如果父线程存在 inheritableThreadLocals 变量且不为空,就调用 ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap 方法为子线程的 inheritableThreadLocals 变量赋值。ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap 方法所做的事情,其实就是将父线程的 inheritableThreadLocals 变量值赋值给子线程的 inheritableThreadLocals 变量。因此,在子线程中就可以访问到父线程 ThreadLocal 中的数据了。
需要注意的是,这种复制不是实时同步,有一个时间节点。在子线程创建的一瞬间,会将父线程 inheritableThreadLocals 变量的值赋值给子线程,一旦子线程创建成功了,如果用户再次去修改了父线程 inheritableThreadLocals 变量的值(即修改了父线程 ThreadLocal 中的数据),此时子线程是感知不到这个变化的。
好啦,经过上面的介绍相信大家就搞清楚 ThreadLocal 和 InheritableThreadLocal 的区别了。
4.SpringSecurity
先来看一段代码:
1 |
|
默认情况下,子线程中方法是无法获取到登录用户信息的。因为 SecurityContextHolder 中的数据保存在 ThreadLocal 中。
SecurityContextHolder 中通过 System.getProperty 来获取默认的数据存储策略,所以我们可以在项目启动时通过修改系统变量进而修改 SecurityContextHolder 的默认数据存储策略:
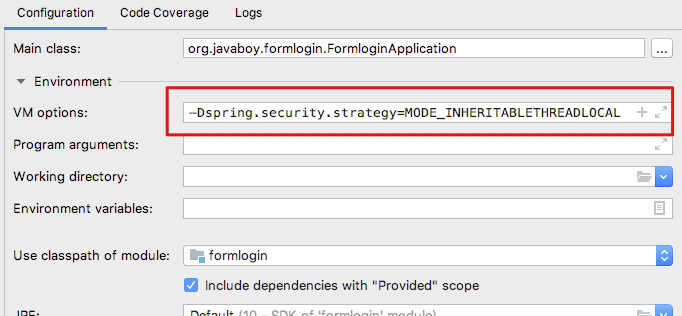
修改完成后,再次启动项目,就可以在子线程中获取到登录用户数据了,至于原理,就是前面所讲的。
5.小结
好啦,今天就和小伙伴们分享一下 SecurityContextHolder 中数据的存储策略问题,感兴趣的小伙伴可以自己试一试~
如果觉得有收获,记得点个在看鼓励下松哥哦~
